A touch screen can feel when you touch it. It does this by noticing changes on its surface. This lets you use your finger to control what you see. The technology puts both input and output in one device. This makes it simple to use phones, tablets, and other digital tools. There are different ways these screens sense touch. Some use capacitive systems, and others use resistive systems. The market for touch screen displays is growing fast. This is because mobile devices are very popular. New improvements in screen technology also help the market grow.
Key Takeaways
- Touch screens know you touched them by noticing changes in pressure, electric charge, light, or sound on their surface.
- There are four main kinds of touch screens: capacitive, resistive, infrared, and surface acoustic wave. Each type has its own special strengths and uses.
- Capacitive screens are quick and accurate. They let you use more than one finger at once. This makes them great for phones and tablets.
- Resistive screens work with anything you touch them with. They are strong, but you have to press down. They only let you use one touch at a time.
- Picking the best touch screen depends on how and where you want to use it. You should think about things like if you wear gloves, how exact you need it to be, and how tough it is.
Touch Screen Basics
How Touch Is Detected
A touch screen senses a finger or object by detecting changes on its surface. Different types of touch screens use unique methods to find where the touch happens.
- Resistive touch screens have two thin layers with a small gap between them. When someone presses the screen, the layers touch and change the electric current. The system measures this change to find the exact spot.
- Capacitive touch screens store electrical charge on their surface. When a finger touches the screen, it takes away some charge. Circuits at the corners measure the difference and locate the touch.
- Surface acoustic wave touch screens use sound waves that travel across the glass. A touch interrupts these waves, and sensors pick up the change to find the location.
- Infrared touch screens use beams of light across the screen. When a finger blocks the light, sensors detect the break and mark the spot.
Each method has its own way of sensing input. Resistive screens work with any object that applies pressure. Capacitive screens need something that conducts electricity, like a finger. Surface acoustic wave and infrared screens can sense most objects, but very small or hard items may not work.
Input and Output Roles
A touch screen combines two main jobs in one device. It acts as both an input and an output tool.
- As an input device, it senses where a person touches and sends this information to the computer or phone.
- As an output device, it shows images, videos, and text for the user to see.
The process starts when a person touches the screen. The system detects the touch and calculates the coordinates. The controller then sends this data to the device’s processor. The processor decides what action to take, such as opening an app or typing a letter. This quick process lets users interact directly with what they see.
Note: The combination of input and output in a single touch screen makes devices easier to use and more interactive.
Touch Screen Technologies

Touch screens use different ways to sense touch. The main types are capacitive, resistive, infrared, and surface acoustic wave. Projected capacitive is a special kind of capacitive screen. It is important in many new devices. Each type works best in certain places and for certain jobs.
Capacitive Touch Screen
Capacitive touch screens work by sensing changes in electrical charge. The screen has a glass layer with a see-through conductor on it. When you touch the screen, your finger takes a little charge. This changes the electrostatic field. The touch controller finds this change fast and locates the touch. This makes the screen respond quickly and accurately. You can use more than one finger at a time.
Most phones, tablets, and laptops use capacitive screens. They show clear images and are good for games, drawing, and typing. These screens do not scratch easily and can handle dust and water. Projected capacitive screens use a grid of electrodes. They can sense many touches at once. They even work if you wear gloves or use a cover.
Tip: Capacitive touch screens are smooth and quick. They are great for devices that need fast and exact input.
| Parameter | Definition / Measurement Method | Importance / Impact on Performance and Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | The biggest error between real and reported finger spot, tested with a fake finger | Makes sure the touch is in the right place; very important for typing and drawing without a stylus |
| Finger Separation | The smallest space between two fingers that the screen can tell apart | Lets you use more than one finger at once, which helps with gestures and typing |
| Response Time | How long it takes from touching the screen to the controller noticing, measured by tools | Decides how fast you can swipe or flick; slow response can make the screen feel jumpy |
| Refresh Rate | How often the screen checks for touch while your finger is on it | Higher rates make gestures smoother and help track motion better |
| Average Power Consumption | Found by multiplying current and voltage, looking at different modes like sleep or wake | Affects battery life and energy use; power changes with how much you use the device |
Resistive Touch Screen
Resistive touch screens work by feeling pressure. The screen has two thin layers with a tiny gap. When you press down, the layers touch and change the resistance. The system checks this change to find where you touched. You can use anything to touch it, like a finger, pen, or glove.
Resistive screens are used in factories, ATMs, and hospitals. They can handle tough places and work with gloves or pens. But you must press hard, and they do not let you use more than one finger at a time. They are less sensitive and can be slower than capacitive screens. Calibration helps them work better.
| Feature | Resistive Touchscreen | Capacitive Touchscreen |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Needs a hard press to work | Very sensitive, works with a light touch |
| Responsiveness | Slower because it needs pressure | Fast and lets you use more than one finger |
| Multi-Touch Support | Usually only one touch at a time | Lets you pinch, zoom, and swipe |
| Input Methods | Works with finger, pen, or gloves | Works best with bare finger |
| Durability | Tough, good for rough places | Not as tough in harsh places |
Infrared Touch Screen
Infrared touch screens use invisible light beams across the screen. Emitters and sensors are on the edges. When something blocks the light, the system finds where it happened. You do not have to touch the screen for it to work.
Infrared screens are good for big displays like whiteboards, signs, and ticket machines. They let you use more than one finger and last a long time. There are no layers to wear out. But dust or bright sunlight can sometimes cause problems.
Surface Acoustic Wave
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) screens use sound waves that move across the glass. When you touch the screen, your finger takes away some of the waves. Sensors notice this and find the touch spot. SAW screens are very accurate and work with fingers, pens, or gloves.
Scientists have made SAW screens better by using vibrations and machine learning. These screens can measure how hard you press and work well when wet. SAW screens are used in museums, fancy stores, and special factories. They are sensitive and can feel pressure, but dirt or rough spots can make them less reliable.
Typical Market Applications
- Consumer electronics: Phones, tablets, and laptops use capacitive screens for quick response and multi-touch.
- Industrial: Machines and control panels use resistive screens because they are tough and work with gloves.
- Retail and point of sale: Touch cash registers and kiosks help customers check out faster.
- Healthcare: Medical screens use touch for easy and clear control.
- Automotive: Car screens use capacitive touch for maps and music.
- Education: Whiteboards and learning tools use different touch screens to help students learn.
| Touchscreen Technology | Working Principle | Advantages | Market Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive | Two layers feel pressure; uses special coatings | Tough, works with gloves or pens, reliable | Factory panels, machine controls |
| Capacitive | Senses changes in electrical charge on the screen | Fast, lets you use more than one finger, clear images | Phones, cars, outdoor and factory use |
| Infrared | Uses a grid of light beams; touch breaks the light | Good for big screens, multi-touch, lasts long | Ticket machines, ATMs, office tools, medical devices |
| Surface Acoustic Wave | Sound waves move across glass and sense touch | Sensitive, works with pens and gloves | Special factory and store uses |
Note: Each touch screen type has its own strengths. The best choice depends on what the device will do and where it will be used.
Key Differences
Sensitivity
Touch screens have different levels of sensitivity. Projected capacitive screens react to very light touches. They let you use more than one finger at once. These screens work even with a cover, but you need bare skin or special gloves. Infrared screens can sense anything that blocks their light beams. They work with gloves and styluses. Surface acoustic wave screens also notice gentle touches. But they do not work with gloves and need to stay clean. Resistive screens need you to press harder and only let you touch one spot at a time.
- Projected capacitive: Very sensitive, multi-touch, needs something that conducts.
- Infrared: Senses any object, works with gloves and styluses.
- Surface acoustic wave: Very responsive, does not work with gloves.
- Resistive: Needs pressure, only one touch at a time.
Accuracy
How accurate a touch screen is depends on its type and how people use it. Capacitive screens are very precise and let you do complex moves. But big fingers or soft skin can make them less accurate. This is called the “fat finger” problem. Studies show people can pick small spots well, especially if the software helps. Resistive screens are less accurate and only notice one touch at a time. Infrared and surface acoustic wave screens are pretty accurate. But dust or dirt can make them work worse.
Tip: Bigger buttons on a touch screen help people touch the right spot. This is extra helpful for people with disabilities.
| Technology | Sensitivity | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitive | Very high | High |
| Resistive | Moderate | Moderate |
| Infrared | High | High |
| Surface Acoustic Wave | High | High |
Durability
People test touch screens by bending, pressing, and scratching them. Capacitive screens have strong glass that does not scratch easily. They last a long time. Infrared screens do not have layers that can wear out. This makes them good for places where many people use them. Resistive screens have plastic layers that can get worn down if used a lot. Surface acoustic wave screens need to stay clean and not get damaged. If they get dirty or scratched, they may not work as well.
- Capacitive: Strong glass, does not scratch easily.
- Resistive: Good for rough places, but plastic can wear out.
- Infrared: No layers to wear out, good for busy places.
- Surface acoustic wave: Needs clean, safe glass.
Glove and Stylus Use
Different screens work with gloves and styluses in different ways. Capacitive screens need something that conducts electricity. Regular gloves do not work unless they have special thread or fabric. Resistive screens work with anything, like gloves or a stylus, because they feel pressure. Infrared screens can sense any object, so they are good for public machines. Surface acoustic wave screens do not work with gloves, but they can sense a stylus or bare finger.
| Feature | Capacitive | Resistive | Infrared | Surface Acoustic Wave |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Works with gloves | Special only | Yes | Yes | No |
| Works with stylus | Special only | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Multi-touch support | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
Note: Picking the best touch screen depends on where you will use it and what tools you need.
Practical Considerations
Multi-Touch
Multi-touch lets a device sense more than one finger at once. Projected capacitive touchscreens find many touches by sensing electric changes. These screens react fast and notice even soft gestures. Multi-touch helps people pinch, zoom, swipe, and turn things on the screen. Devices with this feature can do harder actions that single-touch screens cannot do.
- Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) uses user data to follow actions on different devices and channels.
- MTA gives credit to each touchpoint in a user’s path, using models like first-touch or last-touch.
- Marketers use this information to make campaigns better and learn how people use devices.
- Cross-device tracking shows all user actions, even when switching devices.
Capacitive screens are best for multi-touch. They are very sensitive, react quickly, and show clear pictures. Resistive screens only let you touch one spot and need more pressure.
User Experience
Touch screens change how people use technology. Studies show that touching a device makes it feel easier to use. This makes people like the product more and want to buy it. People who like to touch things enjoy using touch screens and feel more in control. When users can touch and move digital things, they feel like they own them. Haptic feedback and touch features make devices feel special and fun.
Research also shows that better touch screens can make shopping better. People who like to touch things prefer devices they can use with their hands. This makes them happier and sometimes leads to more quick buying.
Common Devices
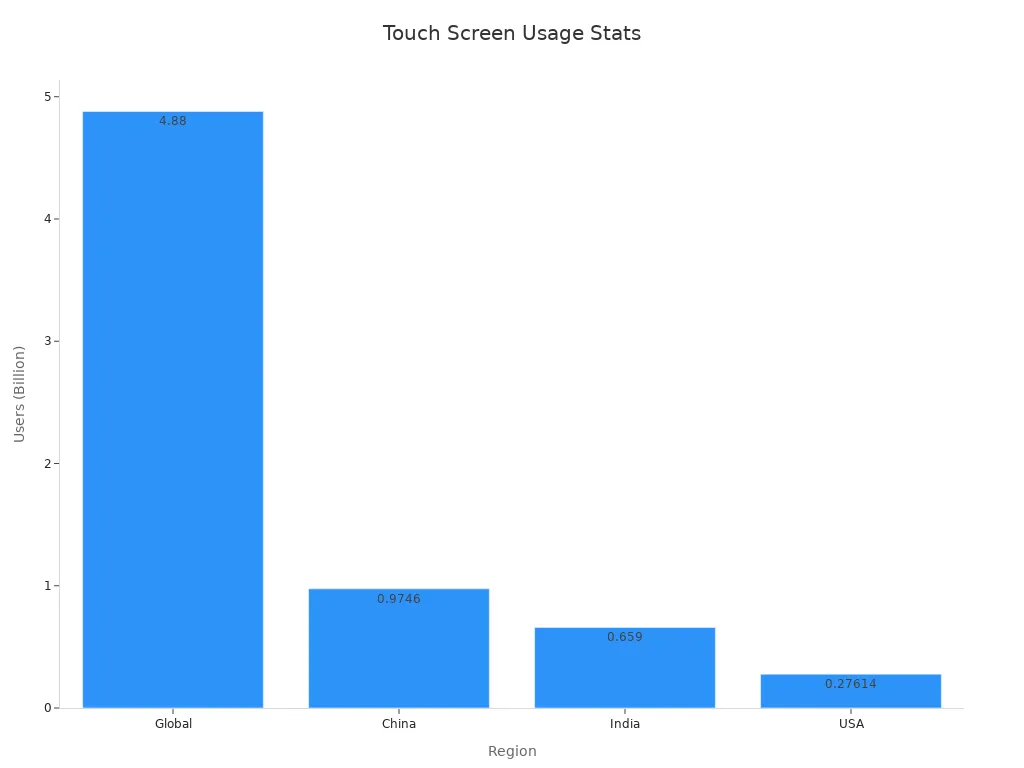
Touch screens are in many devices today. Phones, tablets, laptops, and kiosks all use touch screens. The number of these devices keeps going up. In 2023, companies sent out 1.54 billion touch screens, which is 12% more than last year.
| Metric | Value/Statistic | Notes/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Touch display shipments (2023) | 1.54 billion units | 12% increase from previous year |
| Global smartphone users (2024) | 4.88 billion | About 60.42% of global population |
| Market value (2023) | USD 77.2 billion | Global touch screen display market |
| Projected market value (2032) | USD 158.3 billion | Expected CAGR of 8.3% |
| Leading countries by smartphone users | China: 974.6 million | Key markets for touch screen technologies |
| India: 659 million | ||
| USA: 276.14 million | ||
| Dominant technology segment | Capacitive touch screen technology | Drives significant global revenue |
Capacitive touch screens are the most common. They support multi-touch, last a long time, and cost less. These screens are in most phones and tablets, so they are a big part of daily life.
Touch screens can tell when you touch them in different ways. They sense changes in pressure, electrical charge, light, or sound waves. Each type has its own good points for being accurate and lasting a long time. They also fit different user needs. Studies say touch screens work well in labs and in real life. Market reports show touch screens are growing more popular. They help people work better and make devices simple to use.
- Experts say you should clean your touch screen often. They also say it is best to have a pro set it up.
People should pick a touch screen that fits how they use it and where they use it. This helps them get the best results.
FAQ
How does a touch screen know the difference between a finger and a stylus?
A capacitive screen senses electrical charge from a finger. Most regular styluses do not have this charge. Special styluses work because they conduct electricity. Resistive screens detect pressure, so they work with any object.
Can a cracked touch screen still work?
A cracked screen may still respond to touch if the sensors remain intact. Severe cracks can break the sensors or circuits. This damage can cause dead spots or make the screen stop working.
Why do some touch screens not work with gloves?
Capacitive screens need something that conducts electricity. Most gloves block this signal. Special gloves with conductive material allow the screen to sense touch. Resistive and infrared screens work with gloves because they detect pressure or blocked light.
What is multi-touch, and why is it important?
Multi-touch lets a device sense more than one finger at once. This feature allows users to pinch, zoom, and rotate images. It makes using apps, games, and maps easier and more interactive.
How can someone clean a touch screen safely?
Use a soft, lint-free cloth. Slightly dampen the cloth with water or a screen-safe cleaner. Avoid spraying liquid directly on the screen. Never use harsh chemicals or rough materials.
Tip: Clean screens gently to avoid scratches.
.png)



