Introduction to HDR and Its Importance
HDR (High Dynamic Range) technology is a major advancement in digital visual entertainment. It significantly improves the quality and realism of images in games, movies, and photography. HDR expands the brightness range between the darkest and brightest areas of an image, making visuals more lifelike.
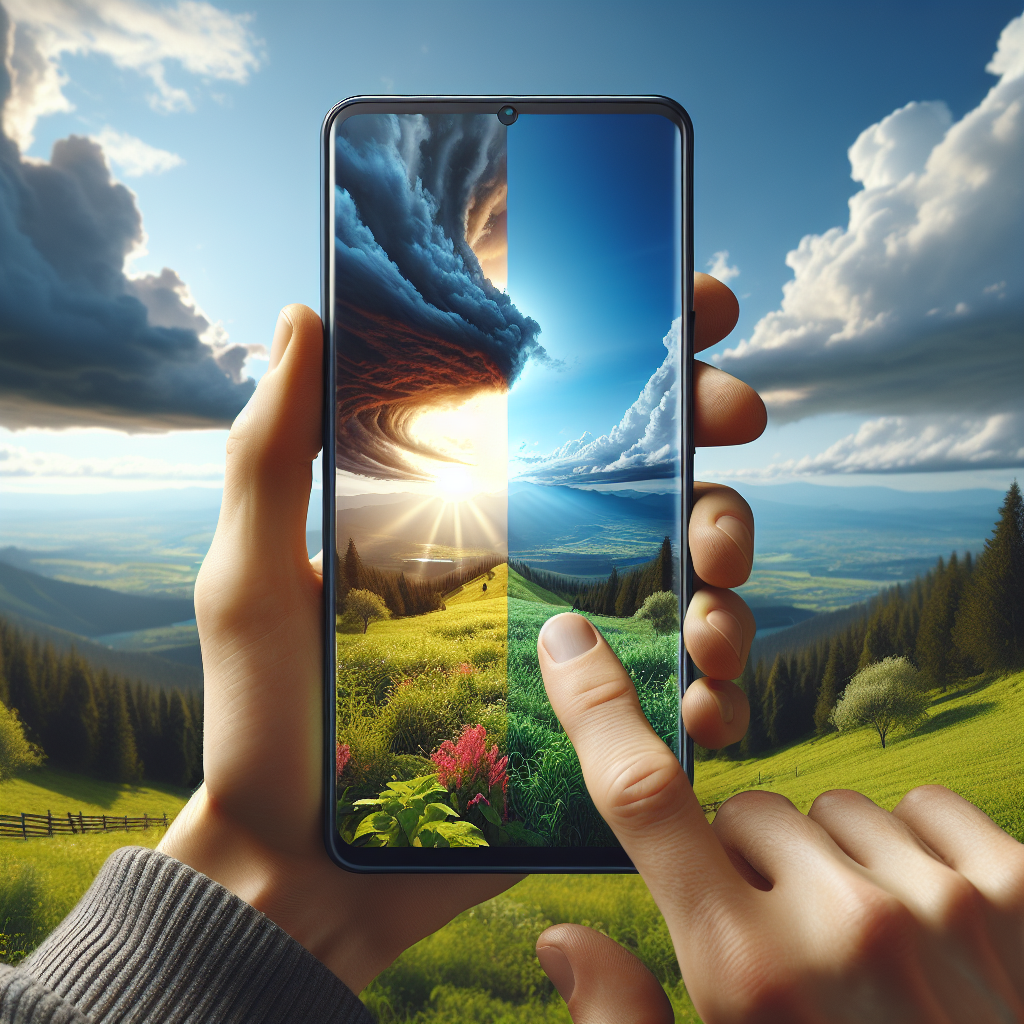

Dynamic Range and Image Quality
Dynamic range refers to the difference between the brightest and darkest parts of a display. Standard screens usually offer 300 to 500 nits of brightness. In contrast, the human eye can perceive up to 20,000 nits. HDR technology brings displays closer to this level of realism.
How Does HDR Work?
HDR enhances each pixel’s color bit depth. Standard images use 8-bit color (256 brightness levels). HDR, however, uses 10, 12, or even 16-bit color, resulting in smoother gradients and a wider color gamut.
HDR Effects: Greater Depth and Realism
With HDR, shadows are deeper and highlights are more brilliant. This results in a more lifelike image. Enhanced contrast allows viewers to see details in both dark and bright scenes that would otherwise be lost.
HDR and HDR10+ Signals – What Are They?
To display HDR content, the source must output a compatible HDR signal. This includes 4K Blu-ray players, next-gen consoles, or HDR-ready streaming platforms. Devices often show HDR format information in their settings or playback menus.
HDR Standards: HDR10, HDR10+, and Dolby Vision
HDR10 is an open standard. HDR10+ and Dolby Vision provide dynamic metadata for frame-by-frame tone mapping, enhancing image accuracy. Dolby Vision supports up to 12-bit color and higher brightness capabilities.
HDR Mode on Smartphones and Cameras
Modern phones and DSLRs often include HDR modes. These modes automatically combine multiple exposures for a wider dynamic range, especially effective in low-light or high-contrast environments.
HDR in Computer Monitors
HDR-ready monitors enhance media consumption and gaming visuals. To benefit from HDR, a display should support at least 500 nits of brightness and HDR10. Games with HDR rendering appear more vivid and immersive.
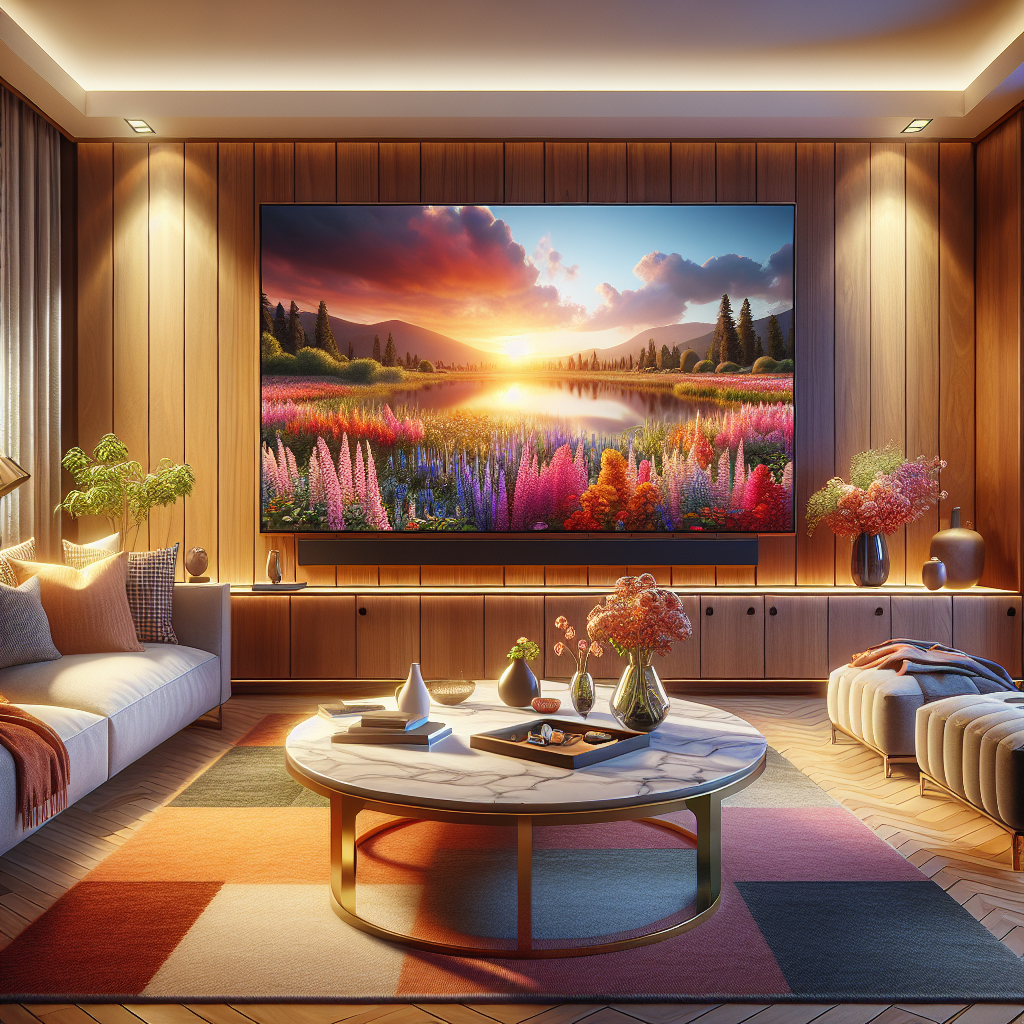

HDR in TVs
HDR TVs offer richer contrast and color depth. To fully enjoy HDR, you’ll need compatible source devices, such as 4K Blu-ray players or HDR-enabled streaming content providers.
HDR Applications in Industry
Beyond entertainment, HDR improves industrial display performance. It enhances clarity and contrast, supporting precise machine control and better HMI readability in fields like healthcare, transportation, and defense.
Conclusion
HDR has transformed the way we experience visuals, whether for entertainment or industrial monitoring. Its enhanced contrast, deeper tone mapping, and broader color representation make it essential in modern display technologies. To fully benefit from HDR, compatible sources and displays are crucial.
Contact our experts — we’ll help you choose the best solution for your needs.
[Contact Us]
.png)