The Evolution of Vehicles: A Look at OLED Displays in the Automotive Industry
Today’s vehicles bear little resemblance to those of our grandparents or great-grandparents. Thanks to technology, travel has become safer, faster, and more modern.
Table of Contents
- OLED Displays in the Automotive Industry
- How Do OLED Displays Work in Cars?
- Advantages of OLED Displays Compared to Traditional LCDs
- OLED vs. LCD: A Comparison
- Examples of OLED Usage on Car Dashboards
- How OLED Displays Improve Driving Safety
With advancements like higher engine efficiency, driver assistance systems, and the integration of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, OLED displays are transforming how we interact with our vehicles. This is just the beginning of how technology is reshaping the driving experience.
OLED Displays in the Automotive Industry
In-vehicle displays are getting larger, and OLED technology helps automakers reduce the weight of these screens. This is crucial in the automotive industry, where saving even a kilogram can increase a vehicle’s driving range.
OLED displays support the growth of electric vehicles (EVs) by enhancing their range without requiring additional battery capacity. Manufacturers can create innovative dashboards with smaller-radius curved screens that reflect their brand identity. These frameless screens seamlessly blend with the vehicle’s design and use less plastic compared to traditional LCDs, making them more environmentally friendly.
How Do OLED Displays Work in Cars?
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. Unlike traditional displays, OLED screens use pixels made of red, green, and blue subpixels that emit their own light, eliminating the need for backlighting. This results in vivid colors and deep blacks.
An OLED display consists of several layers: a substrate, anode, organic layers, conductive layer, emissive layer, and cathode. When electricity flows through the display, electrons move from the cathode to the anode, exciting the organic molecules and causing them to emit light.
Advantages of OLED Displays Compared to Traditional LCDs
One of the key benefits of OLED displays is that each pixel emits its own light. This means they don’t require a backlight, allowing for higher contrast and more vibrant colors.
The increased contrast makes images clearer and easier to read. Additionally, OLED displays provide better viewing angles, maintaining consistent colors even from extreme angles.
OLED vs. LCD: A Comparison
When choosing between OLED and LCD, consider the following:
- Contrast: OLED displays offer significantly higher contrast than LCDs.
- Power Consumption: LCDs consume less power due to their reliance on backlighting.
- Color Accuracy: Both types provide good color accuracy, but OLEDs are often seen as superior.
- Longevity: LCDs typically last longer because their backlights can endure tens of thousands of hours, while OLED materials degrade over time.
- Cost: OLEDs are usually more expensive due to complex manufacturing processes.
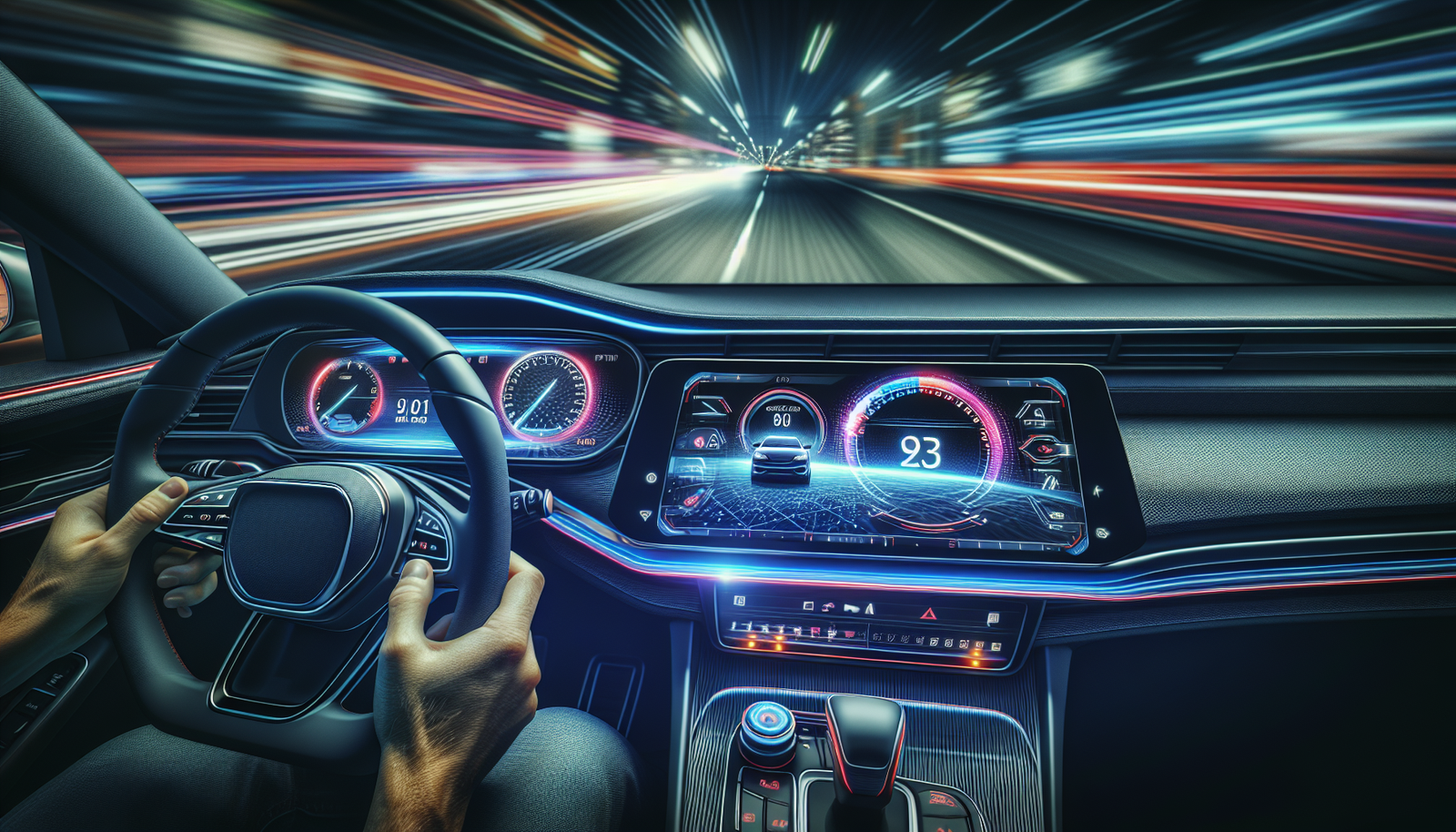
Examples of OLED Usage on Car Dashboards
Many modern vehicles now feature OLED screens for speedometers, tachometers, clocks, and mileage displays. These elements are easily readable in bright sunlight, and their vivid colors enhance navigation and infotainment systems.
Touchscreen interfaces allow drivers to adjust climate and audio systems without needing physical buttons, making in-seat control more convenient. The user interface is intuitive, enabling users to customize the information displayed.
How OLED Displays Improve Driving Safety
OLED displays offer excellent visibility at any time of day, whether driving through dark tunnels or under bright sunlight. Critical alerts, such as lane departure or collision warnings, appear instantly, allowing drivers to react quickly to potential hazards.
High-quality OLED screens with user-friendly interfaces minimize the time drivers spend looking away from the road, enhancing overall safety.
.png)