In today’s industrial world, efficiency and safety are top priorities. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) connect operators with machines, and touch screen HMI systems have quickly become the standard in modern factories. By replacing traditional buttons and switches with intuitive touch panels, companies gain faster control, real-time data visualization, and smarter process management.
According to recent industry forecasts, touch screen HMI solutions are expected to account for more than half of the HMI market by 2025. This growth is driven by the rising demand for automation, IIoT integration, and user-friendly control systems.
In this article, we’ll explain what a touch screen HMI is, how it works, the benefits across industries, and why more businesses are choosing it as the future of industrial automation.

What Is a Touch Screen HMI?
A touch screen HMI lets operators control machines by touching a screen. On the factory floor, these panels are used to run equipment, view live data, and make quick adjustments. They have largely replaced old switches and levers by offering a simpler, more visual way to manage machines—helping teams work faster and more safely.
Modern systems often present information on an industrial touch screen monitor, making critical data easy to see and act upon.
Core Components of a Touch Screen HMI
- Processor
- Display unit
- Input unit (the touch screen itself)
- Communication interfaces
- Data storage
- System software
- Screen configuration / HMI software
The processor interprets touches, runs software, and communicates with the machine. The HMI software builds the user interface, handles data, and defines the control logic—so the entire system feels seamless to the operator. In many projects, the HMI is paired with a touch screen module tailored to the use case.
Touch Screen HMI vs. Traditional Control Panels
| Feature / Functionality | HMI Touch Screens | Traditional Control Panels |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Intuitive touch (phone-like) | Physical buttons and knobs |
| Display Area | Large, clear visual layouts | Small or no display |
| Customizability | Easy to update and reconfigure | Requires hardware changes |
| User Experience | Multi-touch and gestures | Basic button interaction |
| Real-time Data | Live dashboards for fast decisions | Limited or no live data |
| Integration | Connects across systems | Often isolated |
| Total Cost | Higher upfront, lower lifecycle cost | Lower upfront, higher maintenance |
When you move from concept to hardware selection, our industrial touch screen buyer’s guide helps you match HMI size, glass, and touch type to each workstation.
Applications of Touch Screen HMI
Touch screen HMIs have transformed how operators interact with machines. They are used for process control, machine operation, remote monitoring, diagnostics, and data visualization across manufacturing, energy, transportation, healthcare, food and beverage, and smart buildings.

| Industry | Use Case | Touch Screen Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated process control, assembly lines | Faster changeovers, easier training, live data |
| Energy | Plant control, energy management | Real-time monitoring and quick response |
| Transportation | Dashboards, fleet monitoring | Clear displays, instant alerts |
| Medical | Patient monitoring, equipment control | Intuitive use, fewer errors |
| Smart Buildings | HVAC, lighting, security | Central control with remote access |
Process Control
Operators can change setpoints with a tap, track production, and respond quickly to alarms. Capacitive technology is especially intuitive for frequent interactions. For a deeper dive, see our capacitive touch screen insights.
Machine Operation
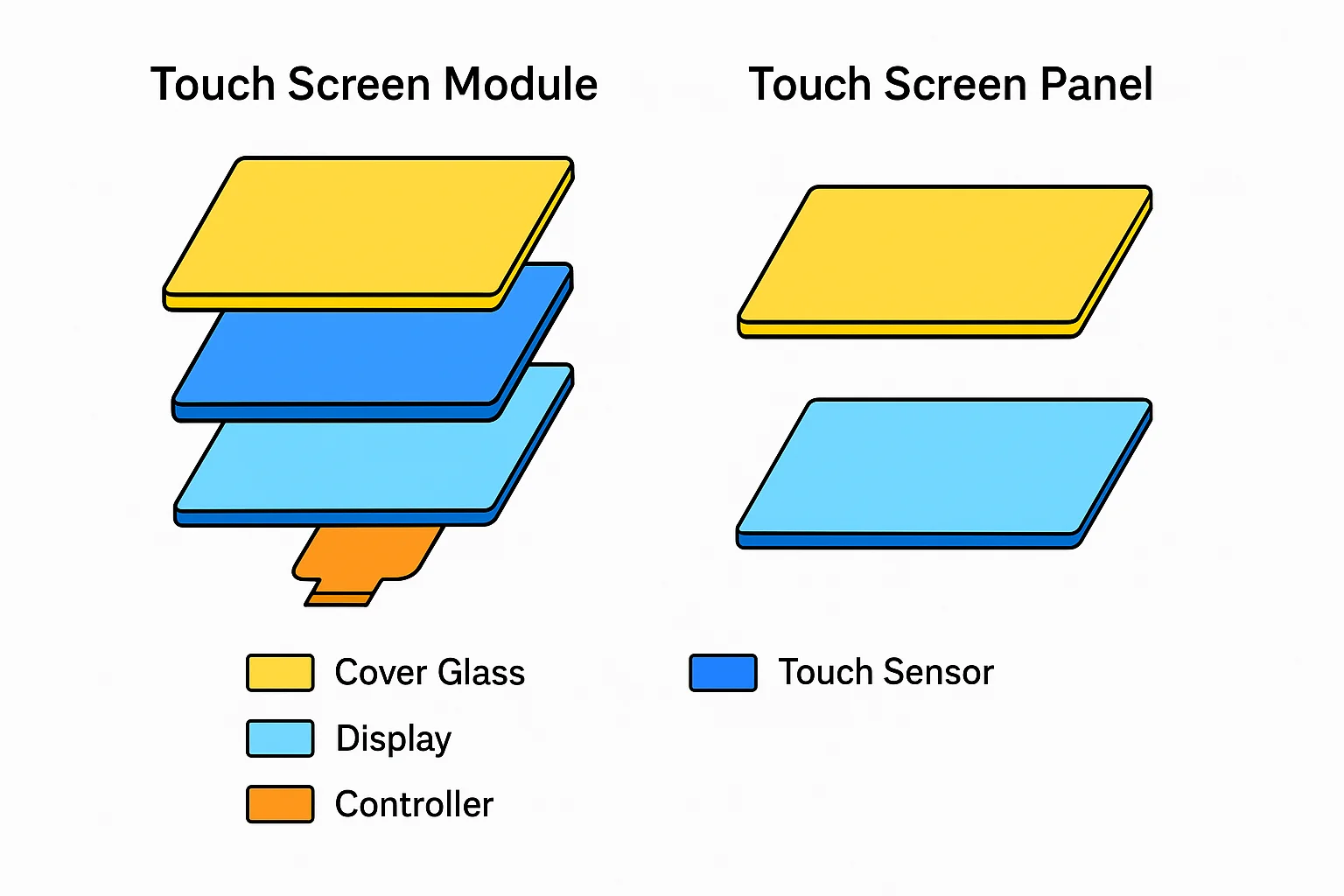
From packaging lines and power plants to building HVAC dashboards, touch panels enable start/stop, mode changes, and recipe selection with simple gestures. Learn more about the difference in our touch screen module vs panel comparison.


Data Visualization
Real-time charts and KPIs speed up decisions. The interface is simple, customizable, and aligned to operator workflows.
Remote Monitoring
Mobile and web-based HMI/SCADA provide live visibility and remote control—shortening response times and reducing downtime. See how this applies in our article on industrial HMI applications.
Diagnostics
Live alarms and guided troubleshooting help teams detect issues early and act before failures escalate.
Benefits of Touch Screen HMI
Efficiency
Faster controls, fewer stoppages, and energy insights lead to measurable productivity gains. For size-related selection, see our guide on industrial touch screen size.
User Experience
Tapping, swiping, and zooming reduce the learning curve and error rates. Clear feedback builds operator confidence.
Flexibility
Layouts and workflows are easy to reconfigure—no new hardware needed. This agility supports continuous improvement.
Safety
Real-time alerts and predictive diagnostics improve response times and help prevent dangerous failures.
Data Integration
HMIs connect to PLCs, databases, and plant systems to centralize insights and accelerate problem solving. See our overview of industrial touch screen options.
Key Features to Consider
Screen Types
- Resistive
- Capacitive
- Near-field imaging
- Infrared
- Ultrasound
For projects that favor clarity and multi-touch, see the capacitive touch panel. For broad project overviews, a general touch screen panel reference can help during early selection.
Durability
| Factor | Capacitive Touchscreen | Resistive Touchscreen |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Thick protective glass | Thinner film layers |
| Scratch Resistance | Glass resists scratches | Film scratches more easily |
| Water & Dust | May register false touches with water | Stable with liquids and dust |
| Temperature | Handles moderate heat | Handles higher heat ranges |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, long life | More frequent upkeep |
Connectivity
Common options include USB, Ethernet, serial ports, Wi-Fi, and HDMI for external displays—useful when pairing with a touch screen module or larger touch screen monitor.
Software Compatibility
Look for broad protocol support (e.g., Ethernet/IP, Profinet, Modbus) and features like scripting, data logging, alarms, and multilingual UI.
Security
- Strong passwords and role-based access
- Encrypted communications
- Regular patches and updates
- Audit logs and intrusion detection
Selection and Maintenance
Choosing the Right HMI
Match screen size and resolution to operator needs. Choose the appropriate touch technology—capacitive for speed and multi-touch, resistive for gloved operation and harsh environments. For deeper background on capacitive technology, review the capacitive touch screen notes.
Implementation Best Practices
- Verify compatibility with PLCs and required protocols
- Select screen size/resolution to fit tasks and space
- Align UI layouts to operator workflows and safety
- Plan for future expansion and reconfiguration
Maintenance
- Clean the screen with a soft cloth (daily/weekly as needed)
- Monitor temperature and humidity; inspect cables and mounts
- Update software and security patches regularly
- Calibrate the touch screen if responsiveness drifts
- Back up configurations and maintain spare parts
FAQ
What is a touch screen HMI?
An HMI that allows machine control via a touch-enabled display—showing data, buttons, and controls for fast, simple operation.
Why use industrial touch screens for HMI?
They improve speed, safety, and decision-making with clear data and intuitive interactions across many touch screen panel applications.
Which is better for HMI: capacitive or resistive?
Capacitive responds quickly and supports multi-touch; resistive works with gloves or stylus. Choose based on environment and task.
Can industrial HMI touch screens work in harsh environments?
Yes. Many models use reinforced glass and high IP ratings suited to dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
How do you maintain an HMI touch screen?
Regular cleaning, periodic calibration, software updates, and routine hardware checks keep systems running smoothly.
Conclusion
Touch screen HMI technology is transforming how industries manage processes, optimize operations, and ensure operator safety. From manufacturing and energy to healthcare and smart buildings, these systems deliver flexibility, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
Ready to evaluate an HMI solution for your facility? Explore our industrial touch screen options and view relevant touch screen modules to match your application. Or contact us to discuss your project.
.png)