Introduction
Industrial displays must ensure excellent readability under harsh conditions such as direct sunlight, dust and water exposure, and vibrations. They must also operate within wide temperature ranges, typically from -20 °C to 70 °C, and resist accidental impacts. Thus, they require robust housings and reinforced screens. This article explores three core data visualization technologies—LCD-TFT, LED, and OLED.
What Display Technologies Are Used in Industrial Monitors?
Three main visualization technologies dominate the industrial market: LCD-TFT, LED, and OLED.
LCD-TFT displays are advanced liquid crystal screens where thin-film transistors control each pixel individually. Even in bright environments, these screens maintain excellent readability thanks to modules with enhanced optical parameters such as brightness and contrast. IPS matrix panels in LCD-TFT displays are notable for offering full viewing angles (89°/89°/89°/89°), allowing consistent visibility from different angles.
LED displays use a matrix of light-emitting diodes, with each diode representing one pixel. These self-illuminating screens ensure high contrast and brightness while being energy efficient. Their modular design allows them to be used for everything from small information displays to large video walls.
OLED displays use organic light-emitting diodes to light each pixel individually, eliminating the need for backlighting. This technology provides deep blacks, high contrast, vibrant colors, extreme temperature tolerance, and outstanding energy efficiency. However, OLED screens may suffer from pixel aging when displaying static content.
Do Industrial Displays Require Anti-Reflective Coatings?
Focusing on LCD-TFT solutions, one challenge is glare in environments such as factory floors where sunlight enters through large windows. Anti-reflective (AR) coatings address this issue. Made of multiple layers of optical materials, these coatings reduce glare and filter specific light wavelengths, making it easier for operators to view screen content.
Why Are Brightness and Contrast Crucial for Industrial Displays?
In LCD-TFT displays, brightness and contrast directly affect image clarity. Proper parameter selection improves visibility and detail distinction.
Brightness levels can reach 1000 cd/m² or higher, ensuring readability even in direct sunlight. This parameter measures the perceived luminance—higher values result in brighter images.
Contrast refers to the ratio between the brightest white and the darkest black a screen can display. A high contrast ratio (e.g., 1000:1) indicates exceptional clarity.
Refresh rate, measured in hertz (Hz), indicates how often the screen updates per second. Industrial monitors typically operate at 60 Hz, sufficient to eliminate noticeable flickering.
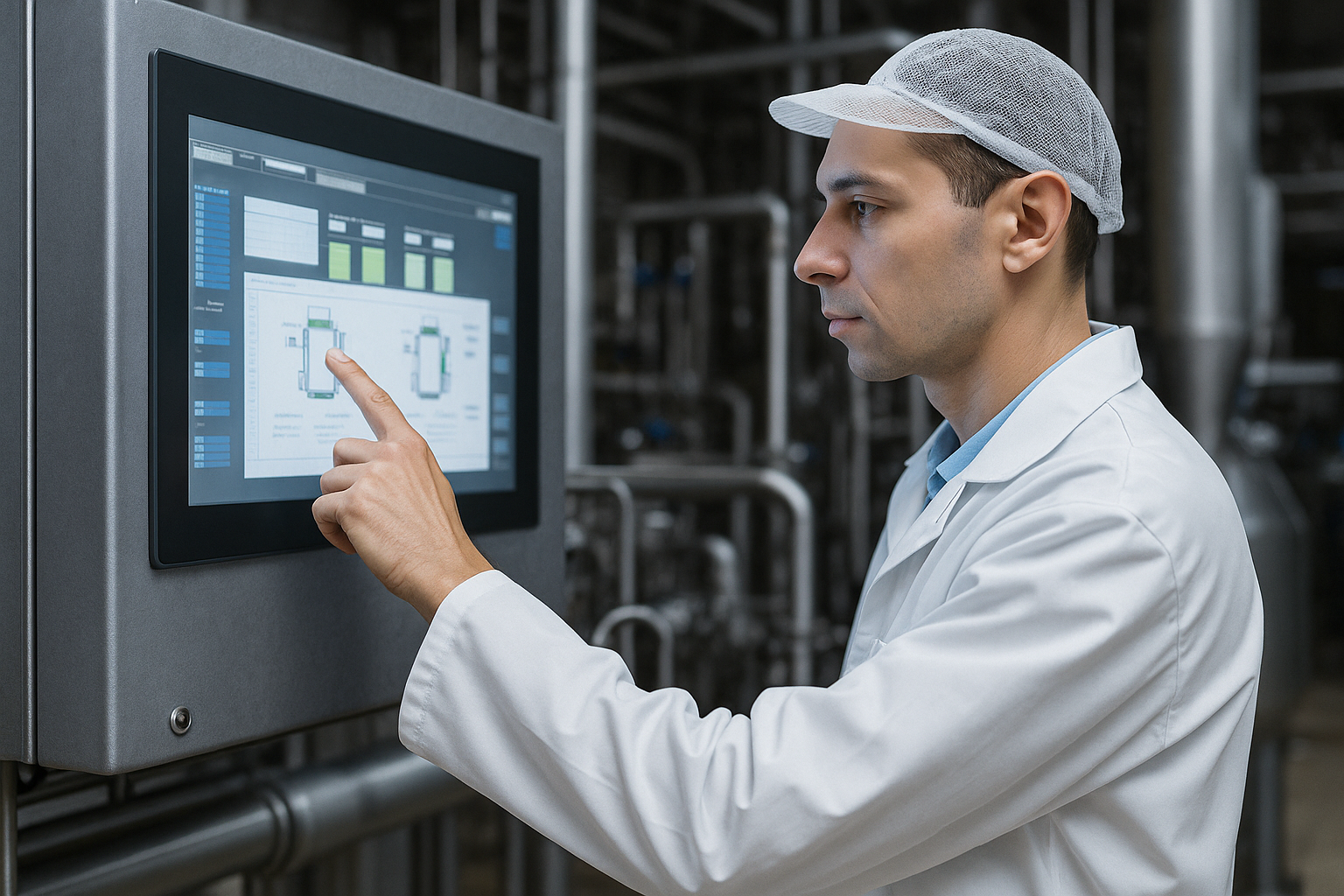
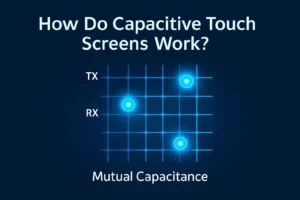
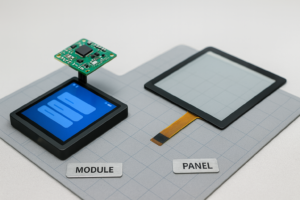
Do Touch Panels Impact Readability?
Touch panels used in industrial displays can affect readability depending on the technology. Resistive touch panels introduce extra layers that may slightly reduce clarity and brightness, potentially causing image distortion.
The choice of screen depends on application. Capacitive touch panels are preferred in industries such as medical or automotive due to superior color fidelity and responsiveness.
Conclusion
For industrial applications, choosing the right display technology is essential for ensuring optimal readability and durability. LCD-TFT with IPS panels, anti-reflective coatings, proper brightness and contrast settings, and the right touch interface can significantly improve the operator experience.
Explore our extensive product catalog featuring LCD-TFT, OLED graphical and alphanumeric displays, LCMs, e-paper displays, barcode scanners, industrial monitors, embedded computers, and various touch panel accessories tailored for demanding environments.
.png)